Theme: Global indagation on SARS-CoV-2 and COVID 19 Hub
Infectious Diseases Meet 2021
About Conference:
Infectious Diseases Meet 2021 program focuses on “Research Reformulate: Develop new methods to detect outbreaks of infectious diseases”. In association with its Editorial Board Members along with institutional partners the Infectious Diseases Meet 2021 embraces various people presenting their research in the procedure of Keynote speeches, Oral Presentations, Video presentations, Symposia, Workshops, Poster Presentations, E-Posters and Exhibitions covering a range of topics and important issues which may be helpful for us all from the research to the practical implementations.
We cordially invite you all the participants from all over the world to attend “4th Global Experts Meeting on Infectious Diseases” are going to be held during May 10-11, 2021, as a Webinar. The Conference highlights the theme “Global indagation on SARS-CoV-2 and COVID 19 Hub ".
Infectious Diseases Meet 2021 is one of the Medical meetings which will be visited by all the research experts, medical educators, research fellow, postgraduates, affiliations, business meanders and various others medical experts from numerous arenas one of them are travel medicine to originates under a solitary rooftop and deliberate various ideas and their researches . Infectious Diseases society meetings will help in B2B teaming up, frameworks organization, amidst specialists and academicians from all corners of the globe.
Infectious Diseases kill more people throughout the world. These infections are mainly caused by germs. We can get infected by touching, eating, drinking or breathing something. Germs can also extent through animal and insect bites, sexual contact. Several of the diseases like measles and chickenpox can also be prevented by vaccines. Hand washing is also used to avoid Infectious Diseases.
The symposium attains consequence when we look at the wide-reaching deaths due to Infectious Diseases. Tetanus (500,000), Measles (1 Million), HIV/AIDS (1 Million), Hepatitis B (1.1 Million), Malaria (2.1 Million), Diarrhea(3.1Million), Tuberculosis (3.1 Million), Respiratory Infections (4.4 Million).
Why to attend Infectious Diseases Conference?
The Infectious Diseases Meet will act as a podium for Infectious Diseases Specialist, Infectious Diseases Researchers, Scientists, Faculties, Students, Business professionals, Healthcare professionals, clinicians, researchers, academicians, foundation leaders, Infectious Diseases Associations and Societies, direct service providers, policymakers, Medical Colleges, Pharmaceutical Companies and Industries, Medical Devices Manufacturing Companies, Drug Manufacturing Companies and Industries and others related to this topic to exchange and deliberate their valuable views on tracking the Infectious Diseases connected concepts.
Infectious Diseases Meet 2021 encourages various methods in the study of large disease burden and highlighting existing opportunities in the field of Public health, Infectious Diseases, Microbiology, Neglected Tropical Diseases, Parasitology, Epidemiology and furthermost importantly about Infectious Diseases, Pediatric Infectious Diseases. Global Infectious Diseases Conferences affords the time to collaborate with industry peers and discover information and resources that can be used to attain your personal and organizational goals.
Infectious Diseases Meet 2021 congregation will strengthen the thoughts about Infectious Diseases and different aspects related to it. We effort to provide a perfect phase to Researchers, Scholars, and key Speakers to share data and involvements and empower people with their deep knowledge of Human Infectious Diseases and seek them to fight against the global risk related to it.
Importance and Scope:
Infectious Diseases are also recognized as communicable Diseases, and the subject of dealing with Infectious diseases is called infectiology, which contracts with the diagnosis, control and action of infections. An infectious disease (ID) specialist's practice may entail mostly of managing nosocomial (hospital-acquired) infections, or it may be out-patient based. ID specialists typically aid as consultants to further physicians in cases of complex infections, and often manage patients with HIV/AIDS and other forms of immunodeficiency. The market report classifies information from diverse sources into a cohesive unit that contains an overview, global implications of infectious diseases, infectious diseases by type, treatment and prevention, emerging pharmaceutical and diagnostic products and a related patents section. Information is systematized by type of infectious disease (i.e., bacterial, viral, parasitic) and proper treatments, both current and anticipated.
In the novel bio-economy, Infectious diseases play a very vital role in representing major global challenges, upgrading waste streams to valuable food constituents, counteracting life-style diseases and antibiotic resistance through the gut biota, making crop plants more confrontation to extreme climatic change conditions, and functioning as host for the production of new biological drugs for treatments of diseases.
Contagion Diseases, Prevention and Control 2021 are giving an international juncture to analysts that afford new insights into the concealed methods of Infection Control. World-eminent speakers, guest of honors, and the most up to date upgrades are particular components of this gathering and with individuals from around the globe concentrated on finding out about uncommon illnesses and its advances; An expanding number of distinguished methods makes it important to complete propelled research here of irresistible sicknesses. Infection Congress 2021 is the utmost chance to do the topmost gathering of associates, conduct presentations, disseminate data, B2B meetings, meet with potential scientists, trade learning on late improvements and make an unmistakable imprint by invigorating development at this event.
Target Audience:
- Microbiologists
- Pathologists
- Epidemiologists
- Dermatologists
- Allergists
- Immunologists
- Pediatricians
- Physicians
- Pharmacists
- Neurologists
- Infection Prevention and Infection Control Specialists
- Academic and Health care Professionals
- Students
- Research Associates
- Health Care Associations & Societies
- Medical & Pharmacy Companies
- Medical Devices and drug Manufacturing Companies
- Laboratory Technicians and Diagnostic Companies
- Business Entrepreneurs and Industrialists
- Tropical Medicine and Infectious Diseases
Associations Related to Infectious Diseases:
- European Society of Clinical Microbiology and Infectious Diseases
- International Union of Microbiological Societies
- Federation of Infection Societies
- Canadian Society of Microbiologists
- British Infection Association
- Federation of European Microbiological Societies
- Welsh Microbiology Association
- Clinical Virology Network
- American Society for Microbiology
- Society for General Microbiology
Track 01: Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases are syndromes triggered by organisms — such as bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites. Many organisms live in and on our bodies. They're normally harmless or even helpful. But under certain environments, some organisms may root disease. Some communicable diseases can be passed from person to person. Some are transmitted by insects or other animals. And you may get others by intense contaminated food or water or being exposed to organisms in the environment. Many infectious diseases cause complications. These can range from mild to severe. For some environments, complications may comprise wheezing, skin rash, or extreme fatigue. Mild complications usually disappear as the infection resolves. Gentle infections might reply to rest and residential remedies, while some serious infections might need hospitalization. Several infectious diseases, like contagious disease and varicella, is prevented by vaccines. Recurrent and thorough hand-washing furthermore helps defend you from most infectious diseases.
Track 02: Epidemiological Diseases
Infectious diseases stay one amid the foremost essential causes of injury and mortality round the world. Furthermore to finding out the rates of and risk issues for communicable disease, ID epidemiologists implement and measure interventions at the individual and community level to: forestall infection (primary prevention) and, among those with contaminations, to forestall expansion of malady (secondary prevention) or disease-associated death and incapacity (tertiary prevention). Infectious diseases stay unique amongst the leading necessary causes of morbidity and mortality round the world.
Track 03: Tropical Infectious Diseases
Tropical infections are diseases that are predominant in or sole to tropical and subtropical regions. The contaminations are fewer predominant in temperate climates, due in part to the occurrence of a cold season, which controls the insect population by forcing hibernation. However, several were existing in northern Europe and northern America in the 17th and 18th centuries before modern understanding of disease causation. The initial impetus for tropical medicine was to defend the health of colonial settlers, notably in India under the British Raj. Insects such as mosquitoes and flies are by far the most common disease transporter, or vector. These insects may transmit a parasite, bacterium or virus that is infectious to humans and animals. Most often disease is communicated by an insect "bite", which grounds transmission of the infectious agent through subcutaneous blood exchange. Vaccines are not available for most of the diseases enumerated here, and many do not have cures. Human investigation of tropical rainforests, deforestation, rising immigration and increased international air travel and other tourism to tropical regions has led to an increased incidence of such diseases to non-tropical countries.
Track 04: Pediatric & Childhood Infectious Diseases
If an adolescent has a mutual or persistent disease prompted by an infectious agent such as bacteria, a fungus, a parasite, or other rare infection, a pediatric infectious diseases specialist has the involvement and qualifications to help pediatrician diagnose and treat the child. Pediatric infectious diseases experts treat children from birth through the teen years. Children are not just small adults. Their bodies are growing and have inimitable medical needs. They frequently express their concerns differently than adults do. Pediatric infectious diseases specialists categorize how to inspect and treat children in a way that makes them relaxed and cooperative. They also recognize the unique signs, symptoms, treatments, and outcomes/prognoses related with infectious diseases in children, which can be quite different from those of adults with such infections.
Track 05: Heart and Cardiovascular Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases of the heart are a assorted and diverse cluster of diseases with variable clinical presentations that may affect the endocardium, myocardium, and pericardium Any type of microorganism can contaminate the heart, including bacteria, fungi, parasites, and viruses, and might affect further than one cardiac structure. Fortunately, almost one-third or more of cardiac infections, including those affecting the myocardium, are supposed to be subclinical and cause minimal or no symptoms. Clinical presentations are usually nonspecific with symptoms ranging from intermittent fever to nondescript chest pain, palpitations, rapid hemodynamic DE compensation, and sudden death. Clinical suspicion is vital for diagnosis, and actual therapy requires identification of the specific organism and its eradication.
Track 06: Blood Infectious Diseases
Blood borne pathogens can cause infections and diseases including HIV, hepatitis, MRSA, and C. diff and can be diffused through contact with an infected individual’s blood or body fluids. The utmost common type of blood contagion is known as sepsis, “a serious complication of septicemia. Sepsis is when inflammation throughout the body occurs. This contamination can root blood clots and block oxygen from reaching vital organs, consequential in organ failure. The National Institutes of Health (NIH) assessments that over 1 million Americans get severe sepsis each year. Amongst 28 and 50 percent of these patients might die from the condition. When the inflammation arises with enormously low blood pressure, it’s called septic shock. Septic shock is fatal in many cases. Blood borne pathogens are infectious microorganisms that are passed in human blood, and they are responsible for blood borne infections and diseases. These microorganisms obligate the potential to pass from one person to another by various routes, such as blood transfusions, sexual intercourse, open wounds, mucous membranes, and more.
Track 06: Infection, Immunity and Inflammation
The Contamination, Immunity and Inflammation Research & Teaching Sector desires to deliver world class interdisciplinary exploration for children with infectious, immunological and inflammatory disease, children with life threatening respiratory disease, youngsters in pain and critically ill children on intensive care. The contact of the immune system with infectious organisms is a vibrant interplay of host mechanisms aimed at eradicating infections and microbial strategies designed to permit survival in the face of powerful defenses. Different types of infectious agents arouse distinct types of immune responses and have evolved unique mechanisms for evading immunity. In some infections, the immune response is the origin of tissue injury and disease.
Track 07: Treatment for Infectious Diseases
Infectious diseases are syndromes triggered by organisms — such as bacteria, viruses, fungi or parasites. Many organisms live in and on our bodies. They're normally harmless or even helpful. But below certain circumstances, some organisms may cause disease. Certain communicable diseases can be passed from person to person. Some are transmitted by insects or other animals. And you may get others by overwhelming contaminated food or water or being open to organisms in the environment. Some of the infectious infections are very mild and cause no harm. However, certain infectious diseases are very severe and can even be dangerous. These diseases can even be diffused from one person to other through numerous means. Some get reassigned via insect or animal bite while some are typically acquired when you ingest contaminated food or water. As there are various pathogens that source infectious diseases, the signs and symptoms also vary based on the pathogen type that has infected you.
Track 08: Infection Prevention, Control and Cure
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), contamination anticipation and control (IPC) is a scientific tactic and practical solution designed to prevent harm caused by infection to patients and health workers. It is a subset of epidemiology, but also aids an essential function in infectious diseases, social sciences and global health. Effective IPC is a public health issue that is essential in patient safety and health system firming. The embarrassment of healthcare-associated infections (HAI), epidemics (including the 2013-2016 Ebola virus disease outbreak), and pandemics of international concern (i.e. 2009 flu pandemic and the coronavirus disease 2019) are entrenched in effective IPC measures. A regulatory principle on WHO's core constituents of IPC is that "access to health care services designed and managed to minimize the risks of avoidable HAI for patients and health care workers is a basic human right".
Track 09: Laboratory Investigation – Infectious Diseases
Laboratory tests might sort organisms directly (Eg, visually, using a microscope, developing the organism in culture) or indirectly (Eg, identifying antibodies to the organism). Some tests (Eg, Gram stain, routine aerobic culture) can sense a large variation of pathogens and are commonly done for many suspected infectious illnesses. However, since assured pathogens are lost on these tests, clinicians must be aware of the limitations of each test for each suspected pathogen. In such cases, clinicians should appeal tests precise for the suspected pathogen (Eg, special stains or culture media) or advice the laboratory of the suspected organism(s) so that it may select more specific tests.
Track 10: Coronavirus COVID-19
Coronavirus disease (COVID-19) is a communicable disease instigated by a newly exposed coronavirus. Furthermost individuals infected with the COVID-19 virus will experience mild to moderate respiratory disorder and recover without requiring special treatment. Older folks and those with underlying medical complications like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, chronic respiratory disease, and cancer are more likely to mature serious illness. The best way to avert and slow down transmission is to be well informed about the COVID-19 virus, the disease it origins and how it spreads. Protect yourself and others from contamination by washing your hands or using an alcohol based rub often and not touching your face. The COVID-19 virus extents generally through droplets of saliva or discharge from the nose when an infected one coughs or sneezes, so it’s important that you also practice respiratory etiquette (for example, by coughing into a flexed elbow).
Track 11: Fungal Infectious Diseases
Fungal infections are mutual throughout much of the natural world. In humans, fungal infections happen when an invading fungus takes over an extent of the body and is too much for the immune system to handle. Fungi can alive in the air, soil, water, and plants. There are also certain fungi that live naturally in the human body. Like several microbes, there are helpful fungi and injurious fungi. When damaging fungi conquer the body, they can be problematic to kill, as they can survive in the environment and re-infect the person trying to get better.
Track 12: Bacterial Infectious Diseases
A bacterial contamination is a proliferation of a dangerous strain of bacteria on or inside the body. Bacteria can infect any area of the body. Pneumonia, meningitis, and food poisoning are just a little illness that might be caused by harmful bacteria. Bacteria originate in three basic shapes: rod-shaped (bacilli), spherical (cocci), or helical (spirilla). Bacteria might also be classified as gram-positive or gram-negative. Gram-positive bacteria require a dense cell wall while gram-negative bacteria do not. Gram staining, bacterial culture with antibiotic sensitivity determination and further tests like genetic analysis are used to identify bacterial strains and help determine the appropriate course of treatment.
Track 13: Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is an umbrella span used to define disorders that encompass chronic inflammation of digestive tract. Types of IBD include:
Ulcerative colitis: This condition comprises inflammation and sores (ulcers) along the superficial lining of large intestine (colon) and rectum.
Crohn's disease: This type of IBD is categorized by inflammation of the lining of digestive tract, which habitually can encompass the deeper layers of the digestive tract.
Track 14: Pulmonary and Chest Infections
A chest infection - affects lungs, either in the larger airways (bronchitis) or in the smaller air sacs (pneumonia). There is a build-up of pus and fluid (mucus), and the airways convert swollen, making it difficult for you to breathe. Chest infections can affect people of all ages. A lung infection can be triggered by a virus, bacteria, and sometimes even a fungus. One of the most common sorts of lung infections is called pneumonia. Pneumonia, which affects the smaller air sacs of the lungs, is most often caused by contagious bacteria, but can also be caused by a virus. A person becomes ill by breathing in the bacteria or virus after a nearby infected person sneezes or coughs.
Track 15: STD and Contact Diseases
Explicitly communicated diseases (STIs) are viruses that are passed starting with one individual then onto the next through sexual contact. The cooperation is generally vaginal, oral, and butt-centric sex. Yet, now and again they can spread through other private actual contact. This is on the grounds that a few STDs, similar to herpes and HPV, are victory by skin-to-skin contact. Now and then these diseases can be moved nonsexual, for example, from mother to baby through pregnancy or labor, or through blood bonding’s or shared needles. People between the ages of fifteen and 24 years get 1/2 every new STD, partner degreed one out of four explicitly dynamic juvenile females has a STD. Notwithstanding, STD rates among seniors square measure expanding.
The global infectious disease therapies market scope was projected at USD 46.88 billion in 2016 and is predictable to grow at a CAGR of 6.6% during the forecast period. The increasing prevalence of infectious diseases, the increase in spending to increase the penetration rate of treatments for these diseases, the increase in awareness initiatives on the treatments and diagnosis of these diseases and the increase in clinical trial studies for the development of new drugs will probably be the responsible factors for the growth of this market.
In addition, the market is likely to witness the expiration of patents of many drugs during the forecast period. The expiration of patents results in the availability of generic drugs, which have the same drug makeup as brand name drugs, but are available at a very low price. Additionally, doctors prescribe these drugs to patients because they are cost effective. Furthermore, a positive reimbursement scenario covering the diagnosis and treatment of these disorders is expected to propel the market growth.
However, the lack of understanding of the treatments for these disorders and the low adoption of treatments are factors that are likely to slow down growth in the years to come. Africa and Asia have a high incidence of infectious disorders and a low rate of treatment penetration for them. According to AVERT, in 2015, 6.5 million people were infected with the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in the West and Central Africa region and 28% of those infected with HIV had access to antiretroviral treatment. Furthermore, increasing availability of counterfeit drugs in Asian countries is expected to pose a significant threat to the market during the forecast period.
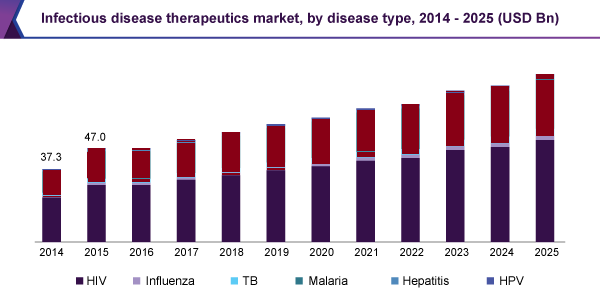
The main players are developing new products for the treatment of infectious diseases and also receive authorizations to market their products. For example, in May 2017, Merck received FDA approval for its ISENTRESS HD, a new 1200 mg integrase inhibitor for patients with HIV-1 infection. This medicine can also be used in combination with other antiretrovirals. In addition, in January 2017, BioCryst received approval from Health Canada for its drug RAPIVAB for the treatment of patients infected with influenza.
Regional Insights:
North America conquered the market in 2016 with a profits share of around 38.6%. The increasing prevalence of these disorders and a favorable reimbursement scenario are key factors likely to propel the demand for infectious disease treatments in the region. In addition, the presence of a large number of manufacturers in the United States and an increasing number of clinical trials for the development of new treatment drugs are expected to contribute to the significant market share held by this region. The major factors likely to propel the growth of this market include the increasing rate of treatment and diagnosis of infectious diseases and increased fundraising activities to support the development of new drugs.
Asia-Pacific is predictable to propagate at the fastest CAGR during the forecast period. High prevalence of HIV, malaria, tuberculosis and other infections; increasing incidence of these conditions; and increasing spending on infectious disease prevention and diagnosis will likely be the major factors responsible for the growth of this market. Besides, the focus by governments of various countries on infection prevention and fundraising to increase uptake of infectious disease treatments is expected to further propel the market during the forecast period.
The majority of people with these infections live in Africa. According to the WHO, in 2015, 90% of deaths from malaria occurred in the African region. Various disease prevention initiatives are underway in the region. In addition, government, private and non-profit organizations are focused on increasing the management of these diseases. For example, Novartis provides free medicines to patients with malaria in the African region.
Conference Highlights
- Infectious Diseases
- Epidemiological Diseases
- Tropical Infectious Diseases
- Pediatric & Childhood Infectious Diseases
- Heart and Cardiovascular Infectious Diseases
- Blood Infectious Diseases
- Infection, Immunity and Inflammation
- Treatment for Infectious Diseases
- Infection Prevention, Control and Cure
- Laboratory Investigation – Infectious Diseases
- Coronavirus COVID-19
- Fungal Infectious Diseases
- Bacterial Infectious Diseases
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease
- Pulmonary and Chest Infections
- STD and Contact Diseases
To share your views and research, please click here to register for the Conference.
To Collaborate Scientific Professionals around the World
| Conference Date | September 13-14, 2021 | ||
| Sponsors & Exhibitors |
|
||
| Speaker Opportunity Closed | |||
| Poster Opportunity Closed | Click Here to View | ||
Useful Links
Special Issues
All accepted abstracts will be published in respective Our International Journals.
- Journal of Infectious Diseases & Therapy
- Journal of Infectious Diseases & Immune Therapies.
- Journal of Infectious Diseases & Preventive Medicine
Abstracts will be provided with Digital Object Identifier by


